Bradyarrhythmia
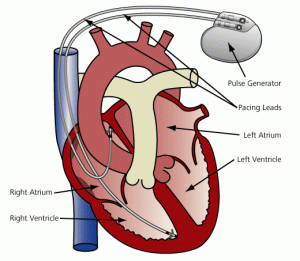
The heart contracts thanks to specialized cellular structures that generate electrical impulses and regulate their distribution in the heart itself.
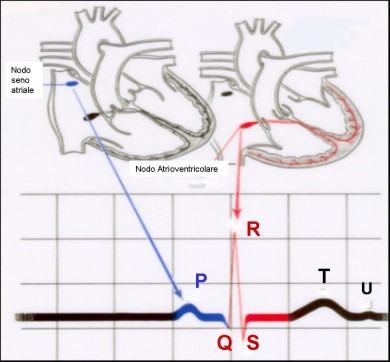
In normal conditions the electrical impulse originates in the atrial sinus node, propagates in the atria and reaches the atrio-ventricular node, which is the only electrical communication path between the atria and ventricles; from here the impulse passes to the His bundle and to the intraventricular conduction system.
Indice dell'articolo
WHAT ARE BRADYARRHYTHMIAS?
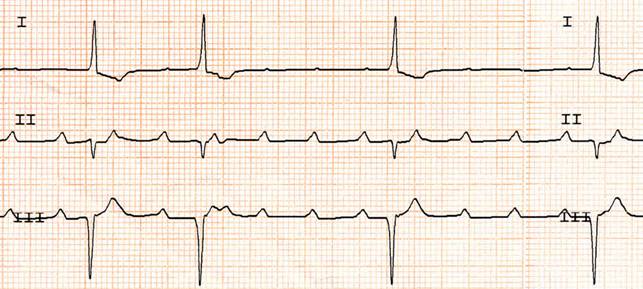
They are heart conditions in which the heart rate is lower than normal. The damage that underlies this arrhythmia can be located at the sinus node (the area that generates the beat) or at the atrioventricular node (the region that allows the transit of the electrical impulse from the atrial to the ventricular chambers).
Bradyarrhythmias therefore include the various forms of sinus node disease and can be characterized by a generalized slowing of the beat or by a sudden absence of the beat itself (in the first case “bradycardia”, in the second case “sinus arrest”).
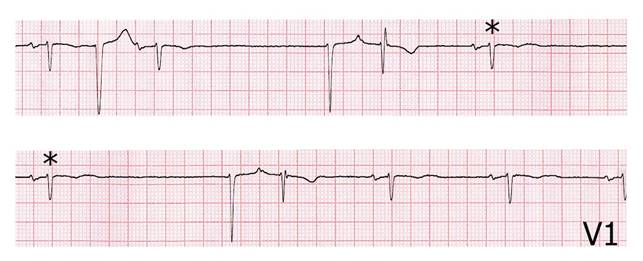
Atrioventricular blocks are conduction disturbances of the electrical impulse at the level of the atrioventricular node.
The atrioventricular blocks are divided by degrees:
- first degree or slowed conduction,wherein all atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles with delay;
- second degree or intermittent conduction, in which some impulses are conducted and others blocked;
• third degree or complete block, in which no atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles.
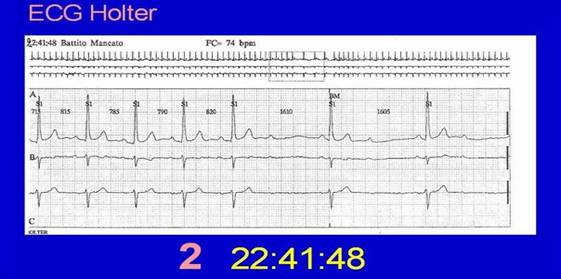
HOW TO RECOGNIZE THEM?
They can manifest with:
• syncope (fainting)
- marked arrhythmia
• dizziness
• asthenia
HOW TO TREAT THEM?
In some cases, bradyarrhythmias are caused by medications and regress when the medications are stopped. In other cases, particularly when bradyarrhythmias cause symptoms, it is necessary to treat them with the implantation of the pacemaker.